A module is a named set of packages designed for reuse. A specification governed by the JCP defines standard packages, and may group them into one or more standard modules.
This Specification groups the standard packages of the Java SE Platform into 21 standard modules, which we refer to as the Java SE modules. The name of a Java SE module always starts with the string "java.". The complete list of such modules is:
java.base
java.compiler
java.datatransfer
java.desktop
java.instrument
java.logging
java.managementjava.management.rmi
java.naming
java.net.http
java.prefs
java.rmi
java.scripting
java.se (aggregator)
java.security.jgss
java.security.sasl
java.sql
java.sql.rowset
java.transaction.xa
java.xml
java.xml.crypto
Compared to Java SE 15, this Specification does not add or remove any modules.
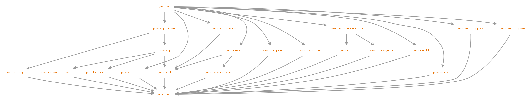
The module graph The Java SE modules depend upon each other as stated in their specifications, which are part of the overall API Specification. The corresponding complete Java SE module graph has too many edges to be displayed easily in visual form; here is the transitive reduction of the directed acyclic graph, in which redundant edges are omitted (click to enlarge):
Here is how to read this visualization of the module graph:
If one module depends upon another, and it grants implied readability to that module via a requires transitive directive, then there is an edge from the first module to the second.
At the very bottom is the java.base module, which contains essential classes such as java.lang.Object and java.lang.String. The base module depends upon no module, and every other module depends upon the base module.
At the top is the java.se module, which gathers together all of the modules that comprise the Java SE Platform. This is an example of an aggregator module, which logically gathers the content of other modules by granting implied readability to them, but adds no content of its own. A run-time system configured to contain the java.se module will contain all of the packages of the Java SE Platform.
A module is a Java SE module — that is, considered part of the Java SE Platform Specification — if and only if it is a standard module reachable from the java.se module.
Relaxing strong encapsulation As an aid to migration, an Implementation may provide a means to invoke its run-time system with one or more packages of one or more of its modules open to code in all unnamed modules, i.e., to code on the class path. If the run-time system is invoked in this way, and if by doing so some invocations of the reflection APIs succeed where otherwise they would have failed, then the first such invocation must cause a warning to be issued on the standard error stream. Later such invocations may also cause warnings to be issued.
(The Reference Implementation provides this capability via the
command-line option --illegal-access=permit.)
An Implementation must not, by default, relax the strong encapsulation of any of its modules. That is, its run-time system must not customarily behave as if various packages in the Implementation’s modules are open when they are not open according to their module declarations. A package, or an entire module, is open to code in all unnamed modules if and only if:
- It is explicitly declared to be open, without qualification, in a module declaration, or
- The run-time system is explicitly invoked to open it to code in all unnamed modules, as provided for below.
A future revision of this Specification is expected to disallow relaxed strong encapsulation entirely.
This section may be compared to the corresponding section that appeared in Java SE 9 through 15.
Incorporated subsections This Specification incorporates the following subsections by reference from Java SE 9 Platform Specification (JSR 379), “Modules”:
- Constraints on Java SE modules
- Constraints on all modules in an Implementation
- Overriding module declarations
- Upgradeable modules
The only upgradeable module in this Platform Specification
is
java.compiler.